Unlocking the Secrets of Our Star: Amazing Facts About the Sun
BlogTable of Contents
- கறிவிருந்தில் மோதல்..திடீரென நடந்த எதிர்பார்க்காத ட்விஸ்ட்.. ஓட்டம் ...
- North Korean becomes 'first man to land on Sun'! - India Today
- 29 | March | 2010 | The Skinny on Science
- Astronomers find that the sun’s core rotates four times faster than its ...
- Pictures of the Sun
- Sun 030912
- Science Trek - Science Trek
- கரகாட்டக்காரன் காமெடியை நினைவுபடுத்தி இபிஎஸ்-ஐ வெளுத்துக்கட்டிய ...
- The Sun 12242023G online video cutter com - YouTube
- போர்க் கப்பலில் இரவில் தரையிறங்கிய மிக்-29 விமானம்.. வெளியானது வீடியோ ...
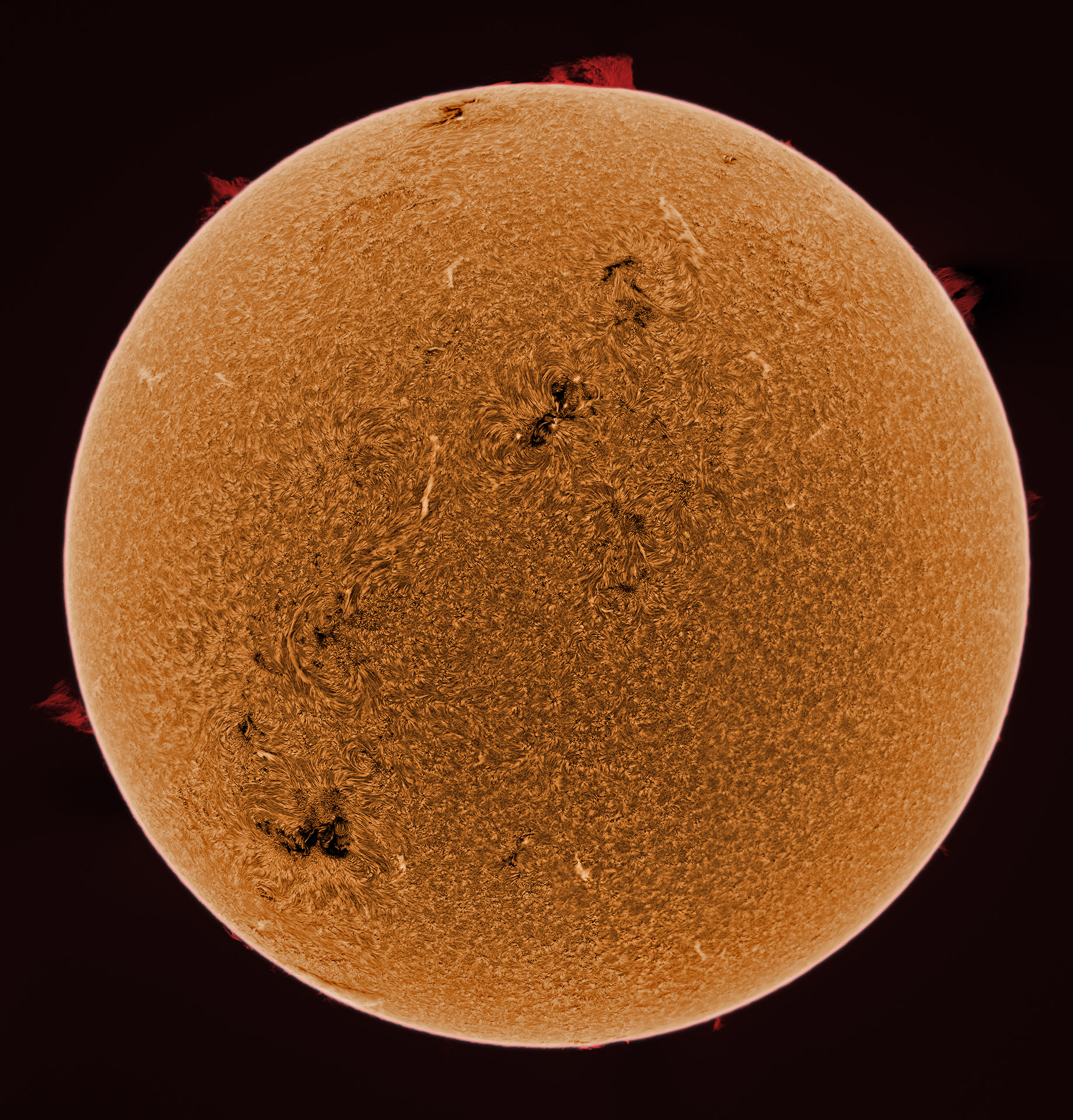


The Sun's Structure



The Sun's Size and Scale


The Sun's Energy Output
The Sun's energy output is staggering, with approximately 3.8 x 10^26 watts of power being released every second. This energy is what makes life on Earth possible, powering photosynthesis, driving the climate and weather patterns, and influencing the formation of our planet's geology. The Sun's energy is also what makes solar power a viable and renewable source of energy for human societies.
The Sun's Life Cycle
The Sun is about 4.6 billion years old and has already burned through about half of its hydrogen fuel. It has about 5 billion more years of life left, after which it will exhaust its fuel and expand into a red giant, engulfing the inner planets, including Earth. Eventually, the Sun will shed its outer layers, leaving behind a white dwarf remnant.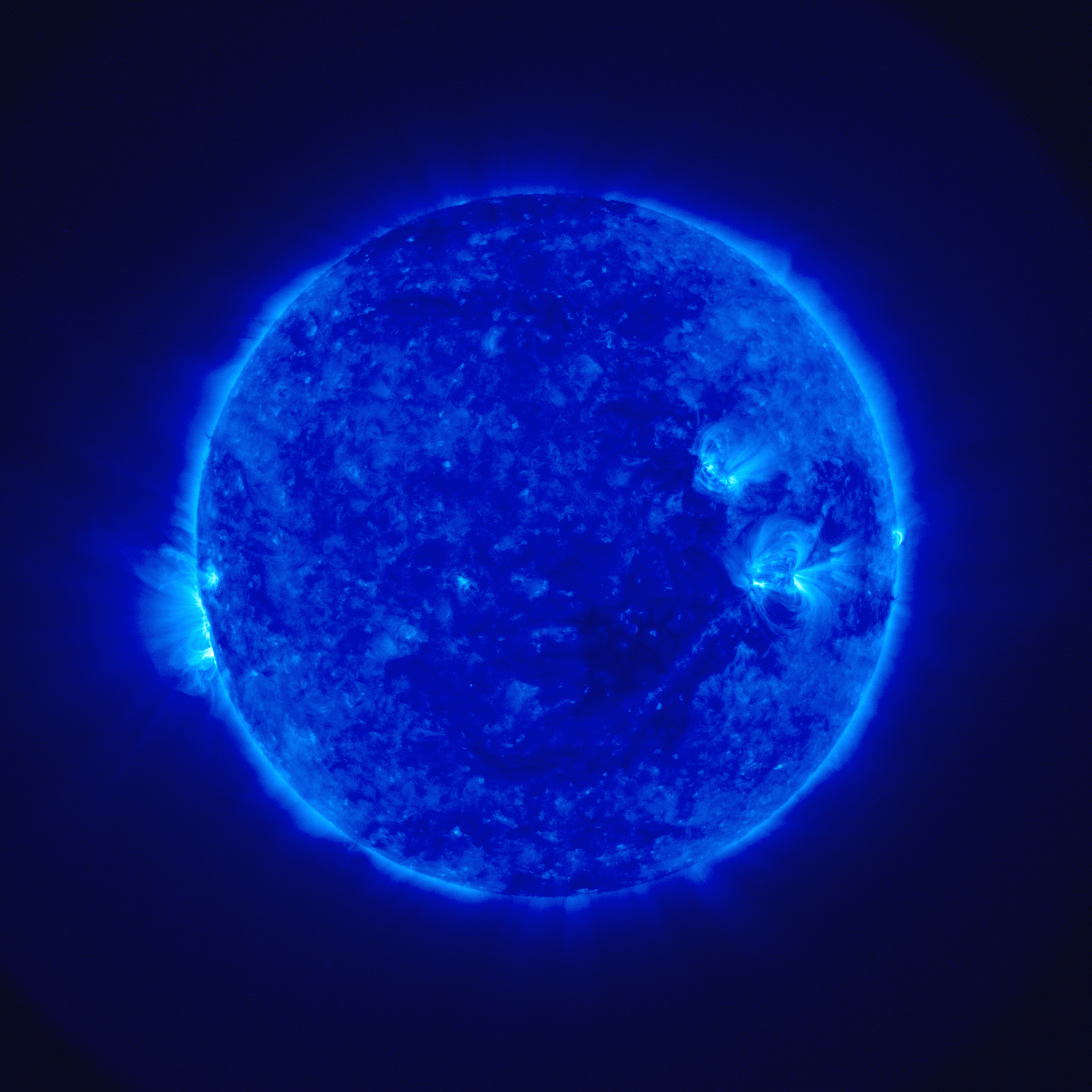
Exploring the Sun with Science@NASA
NASA's Sun-related missions, such as the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and the Parker Solar Probe, have greatly advanced our understanding of the Sun's behavior and its impact on the solar system. These missions have provided valuable insights into the Sun's magnetic field, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections, which affect space weather and have significant implications for satellite communications, navigation, and power grids. The Sun is an awe-inspiring and fascinating celestial body that plays a vital role in our daily lives. By studying the Sun and its behavior, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the workings of our solar system and the universe as a whole. As we continue to explore and learn more about our star, we may uncover even more secrets and surprises that will help us better appreciate the beauty and complexity of the cosmos.Learn more about the Sun and its fascinating facts at Science@NASA. Discover the latest news, research, and missions related to our star and the wonders of the universe.
Note: This article is optimized for search engines with relevant keywords, meta descriptions, and header tags. The content is engaging, informative, and easy to read, making it perfect for online audiences interested in space and science.